1. Integration process
1.1 Import SDK from MavenCentral
Click on the MavenCentral central repository and search for the keyword coraool-android-sdk , as shown below:
1.1.1 Gradle Project
Add dependencies for specified versions in build.gradle
1. 项目中添加从 mavenCentral() 仓库获取依赖
2. 添加依赖
dependencies {
implementation 'com.coraool:coraool-android-sdk:2.0.9'
}1.1.2 Maven Project
Add dependencies for specified versions in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.coraool</groupId>
<artifactId>coraool-android-sdk</artifactId>
<version>${version}</version>
</dependency>1.2 Import SDK from local Lib library
Copy the sdk to the libs directory of the application, and add the dependency of the aar package in the build.gradle of the corresponding module
implementation files("libs/coraool-android-sdk-2.0.9.aar")| SDK Version | VersionDate | Release Notes | Assets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0.9 | 20240820 | Native + JsBridge event trackingRemote interface invocationABTest functionGTX Traffic Tracking |
1.3 Configure SDK
1.3.1 Permission granted
| Permissions | Permission purposes |
|---|---|
| ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE | Detect networking methods, avoid data transmission in abnormal network conditions, save traffic and power. |
| INTERNET | Allow applications to network and send Statistical Data permissions in order to provide statistical analysis services. |
| ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION (optional) | By obtaining location information, anti-cheating functions are provided for developers to eliminate cheating devices; at the same time, the regional distribution data of users is corrected to make the report data more accurate. |
| ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION (optional) | By obtaining location information, anti-cheating functions are provided for developers to eliminate cheating devices; at the same time, the regional distribution data of users is corrected to make the report data more accurate. |
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8"></uses-sdk>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />1.3.1 Configuration obfuscation
If your application uses obfuscation, please add the following configuration to avoid the SDK being mistakenly confused
-keep class com.coraool.** { *; }
-keepclassmembers class * {
public <init> (org.json.JSONObject);
}1.4 Initialization steps
1.4.1 Apply for AK
Before each app is connected, you need to apply for AppId, AppKey, and AppSecret.
1.4.2 SDK Initialization
The interface class provided by the SDK is named com.coraool. CoraoolSDK , and all methods provide services to the outside world through this class.
First, in the onCreate method of the Application, the SDK is initialized using the Token allocated by Coraool :
/**
* Call this method to initialize Coraool SDK when launch the application.
*
* @param application application object
* @param paramProvider interface
*/
public void initialize(Application application, IParamProvider paramProvider);Initialization example:
public class CApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// 用户身份标识请在SDK初始化之前设置,因为后续初始化过程需要用到
CoraoolSDK.setting.setUserId("your_user_id");
CoraoolSDK.setting.setCustomDeviceId("my_unique_device_id");
CoraoolSDK.initialize(this, new IParamProvider() {
@Override
public String getAppId() {
return "${coraool_appId}"; // 在coraool申请
}
@Override
public String getAppKey() {
return "${coraool_appKey}"; // 在coraool申请
}
@Override
public String getAppSec() {
return "${coraool_appSec}"; // 在coraool申请
}
@Override
public boolean isEnableLog() {
return true;
}
});
Logger.getLogger("Application").info("Init coraool sdk done");
}
}1.5 Other SDK configurations
The APIs related to SDK configuration are uniformly managed by the CoraoolSDK.setting interface object
1.5.1 Login User Identification
When the user logs in or out, the login information needs to be updated in real time
/**
* Call this api to update the login account whenever login, logout or switch account.
*
* @param userId login user id
*/
public void setUserId(String userId);1.5.2 Log switch
It is recommended to turn on the log switch during the development stage to facilitate checking the key processes of the SDK and the content of logging. Please turn off this switch before online release to avoid log printing affecting APP performance.
/**
* Turn on this switch in DEBUG mode to trace sdk logs in different levels.
* Turn it off before publishing app to ensure better performance in production situation.
*
* @param enableLog switch
*/
public void setEnableLog(boolean enableLog);1.5.3 Strict mode
It is recommended to turn on the debug mode during the development phase to check whether the use of various event tracking parameters is reasonable. Please turn it off before online release to ensure the stability of the App.
/**
* Enable [StrictMode] will check all api criteria while running and throw errors if wrong.
* It is recommended to turn on strict mode in DEBUG mode and turn it off before publish.
* This will make sure all usages are correct and make the data engineering easier.
*
* @param strictMode default false
*/
public void setStrictMode(boolean strictMode);2. Event tracking interface
2.1 Tracking event tracking
The APIs related to event tracking are managed by the CoraoolSDK.tracker interface object.
2.1.1 Click on event tracking
Interface definition: Add event tracking for click events
/** * Track click event * @param eventName Event name * @param eventValue Event value map */ public void click(String eventName, Map<String, Object> eventValue);
Parameter description:
| Field | Type | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eventName | string | Yes | Event name | Identify where the user operates on the page |
| eventValue | Map<String, Object> | No | Event parameters | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
| eventValue_key | string | No | Event parameter key | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
| eventValue_value | string | No | Event parameter value | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
Example code:
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
eventValue.put("业务参数key1", 200)
eventValue.put("业务参数key2", "业务参数value2")
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click(String eventName, Map<String, Object> eventValue);2.1.2 Exposure event tracking
Interface definition: Add event tracking for module exposure events.
/** * Track expose event * @param eventName Event name * @param eventValue Event value map */ public void expose(String eventName, Map<String, Object> eventValue);
Parameter description:
| Field | Type | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eventName | string | Yes | Event name | Identify where the user operates on the page |
| eventValue | Map<String, Object> | No | Event parameters | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
| eventValue_key | string | No | Event parameter key | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
| eventValue_value | string | No | Event parameter value | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
Example code:
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
eventValue.put("业务参数key1", 200)
eventValue.put("业务参数key2", "业务参数value2")
CoraoolSDK.tracker.expose(String eventName, Map<String, Object> eventValue);2.1.3 Custom event tracking
Interface definition: Add custom event tracking
/** * Track custom event * @param eventName Event name * @param eventValue Event value map */ public void custom(String eventName, Map<String, Object> eventValue)
Parameter description:
| Field | Type | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eventName | string | Yes | Event name | Identify where the user operates on the page |
| eventValue | Map<String, Object> | No | Event parameters | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
| eventValue_key | string | No | Business parameter key | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
| eventValue_value | string | No | Business parameter value | Business parameters associated with the current event for offline analysis |
Example code:
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
eventValue.put("业务参数key1", 200)
eventValue.put("业务参数key2", "业务参数value2")
CoraoolSDK.tracker.custom(String eventName, Map<String, Object> eventValue);2.1.4 Page event tracking
2.1.4.1 Acquisition mode
Interface definition:
public void setPageCollectionMode(int mode);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| mode | Collection method of page events | CoraoolLibConst. PageMode. Manual Manual (default mode)CoraoolLibConst.PageMode.AUTO automatic |
Example code:
// 自动采集选择:仅支持采集activity,在使用AUTO模式时,可以叠加手动模式,实现方式看#自动埋点API
CoraoolSDK.tracker.setPageCollectionMode(CoraoolLibConst.PageMode.AUTO);
//手动采集选择:支持activity和非activity,默认手动
CoraoolSDK.tracker.setPageCollectionMode(CoraoolLibConst.PageMode.Manual);2.1.4.2 Automatic event tracking
Interface Definition: Add event tracking parameter for page events
/** * Add properties to this page which will be submitted in the Page Event. * Example: * When a customer opens a product detail page in a shopping app, we can append * the product itemId to the page event using this method. Later we can do some * analysis based on these properties. * * @param pageObject Activity * @param properties data */ public void updatePageProperties(Object pageObject, Map<String, Object> properties)
Parameter description:
| Method name | Parameter | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| updatePageProperties | pageObject | Page Activity Object | |
| properties | Update parameters | Only applies to the current page |
Sample code
/**
* 添加页面事件的参数,仅对当前页面实例生效
*/
Map<String, Object> properties = new HashMap<>();
eventValue.put("业务参数key1", 200)
eventValue.put("业务参数key2", "业务参数value2")
CoraoolSDK.tracker.updatePageProperties(Object pageObject, Map<String, Object> properties);2.1.4.2 Manual event tracking
Interface definition
1.1 Called when the page is displayed (onResume)
public void trackPageStart(Object pageObject)
1.2 Called when the page is displayed, and specify the page name (onResume) through the API.
public void trackPageStart(Object pageObject, String customPageName);
1.3 Called when the page is displayed, and the page name is specified through the API. It is only required when the page is automatically event tracking (onResume).
public void trackPageStart(Object pageObject, String customPageName, boolean skipPage)
2. Called when the page exits (onPause)
public void trackPageEnd(Object pageObject);
Parameter description:
| Method name | Parameter | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| trackPageStart | pageObject | Page Activity Object | |
| customPageName | Custom page name | ||
| skipPage | Do you want to skip this page event? | Only useful when automatic event tracking on the page is enabled | |
| trackPageEnd | pageObject | Page Activity Object | |
| customPageName | Custom page name |
/**
* 页面展现的时候调用(onResume)
*/
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageStart(homeActivity);
}
/**
* 页面退出的时候调用(onPause)
*/
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageEnd(Object pageObjet);
}2.2 GTX event tracking protocol
Please refer to the
3. Invoke API interface
Coraool SDK provides API-based data services and defines a set of universal and user-friendly interfaces. Initiating an Invoke interface call through Coraool SDK usually involves the following four steps:
3.1 Structure Response
Com.coraool. CoraoolResponse is a encapsulation of the Coraool API protocol, including three fields. If you don’t care about the result of the request, you can directly use this class to receive the request result. If there is business data to be processed, you need to inherit this class, add the result field, and provide getter and setter methods. According to the agreement of the Coraool API protocol, the business parameters returned by the API call will be saved in this Map structure. The SDK will automatically deserialize, which is convenient for the application layer to use directly.
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Type | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| success | boolean | Whether this request is successful | The return result is valid only if this field is true |
| code | int | Error code | 200 indicates success, other values are similar to the definition of http status, if a negative number is returned, it means that the SDK itself has an exception, and the specific error code is defined by the constant of CoraoolResponse |
| message | string | Text description of the request result | It is only used to assist in troubleshooting the request process and cannot be used for business logic judgment. It always returns "SUCCESS" when the request is successful. If there is an error or exception in the request, the corresponding error description information is returned, which can be used for troubleshooting or feedback to technical support. |
| result | any | Custom business data types | If you need to pay attention to the result of the request, according to the agreement of the Coraool API, the data will be saved in a JSON object with result as the key |
Example code:
public class CoraoolRankingResponse extends CoraoolResponse {
// RankingData表示具体的业务数据
public RankingData result;
public RankingData getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(RankingData result) {
this.result = result;
}
}
public class RankingData {
public JsonArray ranking;
public JsonObject track;
public String version;
}3.2 Construction Request
By creating an object of type CoraoolRequest, construct request parameters that comply with the Coraool API protocol
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Type | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| apiName | string | Interface name | Business interfaces registered on the Coraool open API, such asopen.coraool.home.game.ranking |
| apiVersion | string | Interface version | A business version registered on the Coraool open API, such as 1.0.0 |
| data | any | Request parameters | Specific request parameter object |
| connectTimeout | int | Link timeout, in milliseconds | Network connection timed out |
| readTimeout | int | Read timeout, in milliseconds | Return data stream read timeout |
| callbackOnMainThread | boolean | Callback switch of main thread | Whether to call back to the UI main thread, the default is true. For data that is not directly displayed, it is recommended to set it to false to allow the request to call back to the background thread for convenient secondary processing of the data |
Example code:
CoraoolRequest request = new CoraoolRequest();
request.setApiName("open.coraool.home.game.ranking");
request.setApiVersion("1.0.0");
request.setCallbackOnMainThread(true);
request.setReadTimeout(3 * 1000);
request.setData(new HashMap<String, Object>(){{
put("userId", "登录用户ID");
put("afId", "appsFlyer的ID");
put("deviceId", "设备ID");
}});3.3 Initiate a request
The request API of the SDK is divided into synchronous requests and asynchronous requests, which are uniformly encapsulated under the interface object of CoraoolSDK.api
3.3.1 Synchronization request
Interface definition:
/**
* Send a coraool request synchronously.
*
* @param clz Response class type
* @param request request complies with coraool api protocol
* @return response complies with coraool api protocol
* @param <T> { body }
*/
public <T extends CoraoolResponse> T syncInvoke(Class<T> clz,
CoraoolRequest request)
/**
* Send a request synchronously. If the callback interface is provided,
* the interface will be invoked before this method returns.
*
* @param clz Response class type
* @param request request complies with coraool api protocol
* @param callback callback when done
* @return response complies with coraool api protocol
* @param <T> { body }
*/
public <T extends CoraoolResponse> T syncInvoke(Class<T> clz,
CoraoolRequest request,
CoraoolNetCallback<T> callback)Parameter description:
| Parameter name | Type | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| clz | Class<T> | Return the class of the object class. | Class corresponding to the first step Reponse object class |
| request | CoraoolRequest | Request parameters | Corresponding to the second step request parameter object |
| callback | CoraoolNetCallback<T> | Callback | If the Callback interface parameter is provided, this request will always call back to a method in the Callback interface. The definition of the interface method can be found in the next step |
Return value description:
| Return value | Type | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| response | <T extends CoraoolResponse> | Return object class | Corresponding to the object instance of the first step Reponse, null will only appear when the object cannot be instantiated by reflection, so be sure to keep the parameterless constructor |
Example explanation:
private void syncRequest() {
CoraoolRequest request = new CoraoolRequest();
request.setApiName("open.coraool.home.game.ranking");
request.setApiVersion("1.0.0");
request.setData(new HashMap<String, Object>(){{
put("userId", "123");
put("afId", "afIdx");
put("deviceId", "devicedevice");
}});
CoraoolRankingResponse response = CoraoolSDK.api.
.syncInvoke(CoraoolRankingResponse.class, request);
}3.3.2 Asynchronous request
Interface definition:
/**
* Send a request asynchronously. If the callback interface is provided,
* the interface will be invoked before this method returns.
*
* @param clz Response class type
* @param request request complies with coraool api protocol
* @param <T> { body }
*/
public <T extends CoraoolResponse> void asyncInvoke(Class<T> clz,
CoraoolRequest request)
/**
* Send a request asynchronously. If the callback interface is provided,
* the interface will be invoked before this method returns.
*
* @param clz Response class type
* @param request request complies with coraool api protocol
* @param callback callback when done
* @param <T> { body }
*/
public <T extends CoraoolResponse> void asyncInvoke(Class<T> clz,
CoraoolRequest request,
CoraoolNetCallback<T> callback)Parameter description:
| Parameter name | Type | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| clz | Class<T> | Return the class of the object class. | Class corresponding to the first step Reponse object class |
| request | CoraoolRequest | Request parameters | Corresponding to the second step request parameter object |
| callback | CoraoolNetCallback<T> | Callback | If the Callback interface parameter is provided, this request will always call back to a method in the Callback interface. The definition of the interface method can be found in the next step |
Example explanation:
private void asyncRequest() {
CoraoolRequest request = new CoraoolRequest();
request.setApiName("open.coraool.home.game.ranking");
request.setApiVersion("1.0.0");
request.setCallbackOnMainThread(true);
request.setReadTimeout(5 * 1000);
request.setData(new HashMap<String, Object>(){{
put("userId", "123");
put("afId", "afIdx");
put("deviceId", "devicedevice");
}});
CoraoolSDK.api.asyncInvoke(CoraoolRankingResponse.class, request, new CoraoolNetCallback<CoraoolRankingResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(CoraoolRankingResponse response) {
Log.e("TAG", "Success: " + JSON.toJSONString(response));
}
@Override
public void onFailed(int code, String message) {
Log.e("TAG", String.format("Failed: code=%d, message=%s", code, message));
}
@Override
public void onSystemError(int code, String message) {
Log.e("TAG", String.format("Error: code=%d, message=%s", code, message));
}
});
}3.4 Interface callback
Interface callbacks are used to receive correct and abnormal results
| Interface | Parameter | Type | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| onSuccess | response | T | Return the type of object | Return when the request is processed correctly, corresponding to success = true. |
| onFailed | code | int | Request error code | Corresponding to the scenario where success = false, if the signature is incorrect, invalid token, etc. |
| message | string | Error description | ||
| onSystemError | code | int | Request error code | Various system errors, such as network disconnection, authorization error, data parsing exception, etc |
| message | string | Error description |
public interface CoraoolNetCallback<T> {
/**
* Totally success including network and business
*
* @param response response body {@link CoraoolResponse}
*/
void onSuccess(T response);
/**
* Send request successfully but the response data contains business error, like
* invalid appKey, signature mismatch, params illegal and so on.
*
* @param code error reason code leverages http status definition
* @param message plaintext explaining the error reason.
*/
void onFailed(int code, String message);
/**
* Errors like network not connected, auth error, protocol error and so on
*
* @param code {@link CoraoolLibConst}
* @param message plaintext explaining the error reason.
*/
void onSystemError(int code, String message);
}4. Abtest interface
ABTest related APIs are managed by the CoraoolSDK.ab interface object.
4.1 Initialize Abtest function
By overloading the com.coraool. IParamProvider interface’s isEnableAbtest method, you can enable the Abtest function. Note:
- The function of the Abtest module is turned on by default.
- The user identity will be used for experimental bucketing calculations, so parameters like userId need to be set as early as possible, and it is recommended to complete them before calling the initialize method
public class CApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// 用户身份标识请在SDK初始化之前设置,因为后续初始化过程需要用到
CoraoolSDK.setting.setUserId("123abc");
CoraoolSDK.setting.setCustomDeviceId("my_unique_device_id");
CoraoolSDK.initialize(this, new IParamProvider() {
...
// 通过重载此方法,开始Abtest模块功能
@Override
public boolean isEnableAbtest() {
return true;
}
});
}
}4.2 Get single experiment bucketing
Interface definition
public String getABTest(String experimentName)
Parameter description
| Parameter | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| experimentName | Experiment name | Experimental name created on the experimental platform |
Sample code
String bucket = CoraoolSDK.ab.getABTest("HP_SEARCH_ENTRY_POS");
if ("bucket_a".equals(bucket)) {
// do something for a
} else if ("bucket_b".equals(bucket)) {
// do something for b
}4.3 Get single experiment bucketing object
Interface definition
public CoraoolABTest getABTestObject(String experimentName)
Parameter description
| Parameter | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| experimentName | Experiment name | Experimental name created on the experimental platform |
Sample code
CoraoolABTest abtest = CoraoolSDK.ab.getABTestObject("HP_SEARCH_ENTRY_POS");4.4 Get all experiment bucketing
Interface definition
List<CoraoolAbtest> getABTestListAll()
Parameter description
| Parameter | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| No | No | No |
Sample code
List<CoraoolABTest> buckets = CoraoolSDK.ab.getABTestListAll();AndroidGTX Docking Manual
1. GTP/GTC traffic tracking
GTX event tracking is used for tracking and analyzing page traffic, and can solve the following key business problems:
- Calculate basic indicators such as PV and UV on designated pages.
- Track the source and destination of page traffic, analyze the traffic funnel of user paths.
- Based on traffic and conversion evaluation, inform the business side of the traffic efficiency of each page and the pits within the page.
- Global Tracking Position (GTP): A global location tracking model used to track locations and the flow of traffic between different locations.
- Global Tracking Content (GTC): A global content tracking model used to track delivery content and guide conversion efficiency.
- Global Tracking X (GTX) refers to a solution composed of GTP and GTC.
- pageName: The event name of the page event
1.1 GTP parameter definition
GTP parameter definition: a.b.c.d = ${appId}. ${pageName}. ${module}. ${point} , GTP needs to be constructed and used strictly according to the following specifications. The UI layer constructs these four layers of structure through structured data (it is recommended to use this method), or it can be constructed manually.
| GTP | Meaning | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| A bit | ${appId} | Independent allocation on different ends, corresponding to the appId of SDK initialization parameters, globally unique |
| Bit | ${pageName} | Specified and requested by the product, unique within the current ${app}, b-bit maintained by the access party, registered through documents or systems |
| C position | ${moduleId} | The floor or block number of the page, unique within the current page ${pageName} |
| D position | ${pointId} | The point number of the subdivision within the floor is unique within the current module ${moduleId} |
1.2 GTC parameter definition
GTC parameter definition: a.b.c.d = ${sysId}. ${algoId}. ${algoVer}. ${audienceId} , GTC also includes 4 layers of structure, defined at different levels
| GTC | Meaning | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| A bit | ${sysId} | Delivery system ID, used to identify different content delivery parties |
| Bit | ${algoId} | Delivery algorithm ID, used to identify the delivery algorithm that generates different content for the delivery system |
| C position | ${algoVer} | Delivery algorithm version ID, used to identify different versions of the delivery algorithm |
| D position | ${audienceId} | Delivery audience ID, used to identify different delivery audience |
2. Event tracking access
2.1 Event tracking timing description
Each page event includes: [Start – > Process – > End] these three stages, each stage needs to strictly call the API method of CoraoolSDK according to the document description, so that the interval of each page event is completely closed, and the final page event will form a sequence to express the user’s movement line.
Firstly, it is necessary to define what a page is. From the user’s perspective, a page should be a screen of content that users see on their mobile phones. Typical examples include: search results page implemented by Activity, details page implemented by Activity, and venue page implemented by Fragment with multiple tabs. Each tab can also be defined as a page. Please follow the definition of your product or business to divide the page.
The following explains when the event tracking API should be called according to different page definitions. Please pay attention to the red line in the following figure.
暂时无法在Lark文档外展示此内容
2.2 GTX parameter passing method
After introducing the timing of GTX calls above, this section explains how to pass GTX parameters from one page to another. Because the Android system provides multiple parameter passing methods, different types of pages are not the same, so the parameter passing methods of the two pages need to be agreed upon in advance. Below are explanations for Activity and Fragment respectively.
2.2.1 Activity page parameter passing
Method 1 : Through Intent #putExtra (key, value) , parameters can be passed from FromActivity to ToActivity. For CoraoolSDK, we define CoraoolLibConst. KEY_GTP and CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC two constants Key as conventions, ToActivity will try to read the values of these two keys:
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
// 把GTX参数从FromActivity传到ToActivity,这样ToActivity读取KEY_GTP/KEY_GTC就可以知道页面来源
Intent intent = new Intent(FromActivity.this, ToActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, "四位gtp构成的值,指代当前页面");
intent.putExtra(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前内容");
FromActivity.this.startActivity(intent);
}Method 2 : Through Intent #setData (Uri) , parameters can be passed from FromActivity to ToActivity. For CoraoolSDK, we define CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP and CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC two constants Key as conventions, ToActivity will try to read the values of these two keys:
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
// 执行切换Activity
Uri uri = Uri.parse("protocol://your.uri?k1=v1&k2=v2").buildUpon()
.appendQueryParameter(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, "四位gtp构成的值,指代当前页面");
.appendQueryParameter(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前内容");
.build();
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
}Method 3 : By adding gtp and gtc parameters to the click event, the system will automatically capture gtp and gtc in the click event as the source of the page
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "item", "1");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, "四位gtp构成的值,指代当前页面");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前页面");
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click("GotoNextActivity", eventValue);
// 执行切换Activity
Intent intent = new Intent(FromActivity.this, ToActivity.class);
FromActivity.this.startActivity(intent);
});CoraoolSDK supports these three kinds of parameter transfer methods at the same time. When using them, choose one of the three. If there are multiple, the priority is: Method 1 > Method 2 > Method 3
For most scenarios, the third access method is optimized by only focusing on the corresponding click event. The first/second method requires users to have a deeper understanding of the principles of GTP/GPC.
2.2.2 Passing parameters on fragment page
Through Framgent.setArguments (Bundle) , parameters can be passed from FromFragment to ToFragment. For CoraoolSDK, we define two constants Key : CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP and CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC as conventions. ToFragment will try to read the values of these two keys:
Method 1 : Through Bundle #putString (key, value) , parameters can be passed from FromFragment to ToFragment. For CoraoolSDK, we define CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP and CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC two constants Key as conventions, ToFragment will try to read the values of these two keys:
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Fragment toFragment = new Fragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前页面");
bundle.putString(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前内容");
toFragment.setArguments(bundle);
// 执行切换Fragment
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, toFragment)
.commit();
}Method 2 : By adding gtp and gtc parameters to the click event, the system will automatically capture gtp and gtc in the click event as the source of the page
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "item", "1");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, "四位gtp构成的值,指代当前页面");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前页面");
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click("GotoNextFragment", eventValue);
// 执行切换Fragment
Fragment toFragment = new Fragment();
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, toFragment)
.commit();
});2.2.3 Passing parameters to TabView
Pages with TabView as the container do not have a standard lifecycle similar to Activity and Fragment, and need to add gtp and gtc parameters by clicking, similar to the way #Activity page passes parameters 3;
Method 1 : By adding gtp and gtc parameters on the click event, the system will automatically capture gtp and gtc in the click event as the source of the page
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "item", "1");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, "四位gtp构成的值,指代当前页面");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值,指代当前页面");
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click("GotoNextView", eventValue);
// 此处执行切换到下一个TabView的代码实现// 注意:TabView也需要执行在显示和隐藏的时候分别调用 trackPageStart 和 trackPageEnd
...
});2.3 GTX event tracking interface
2.3.1 Start of the page
Interface definition:
/* Record page starts */ Public void trackPageStart (Object pageObject); Record page start and customize page name. Public void trackPageStart (Object pageObject, String customPageName); Record page start and customize page name, only use when automatic event tracking is enabled. Public void trackPageStart (Object pageObject, String customPageName, boolean skipPage);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Type | Explanation | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pageObject | Activity、Fragment、 WebView | Current Page Object | Yes | If it is an Activity, pass in an Activity object instance.If it is a Fragment, pass in the Fragment object instance.It is strongly recommended to implement the ICoraoolPage interface for Activity and Fragment, and define pageName in the interface method to unify the naming method |
| customPageName | string | Custom page name | No | If Page Object does not implement the ICoraoolPage interface, the page name can be customized through this imported parameter. Otherwise, the SDK will default to the class name as the page name, and the interpretability of event tracking verification is poor |
| skipPage | boolean | Whether to skip the current page | No | It only makes sense when using Activity as the page and enabling automatic page event tracking. Should this parameter not be set for others? |
Example code:
public class MyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ICoraoolPage {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
CoraoolSDK.tracke.getInstance().trackPageStart(this);
}
}2.3.2 Add page parameters
Interface definition:
public void updatePageProperties(Object pageObject, Map<String, Object> properties);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Type | Explanation | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pageObject | Activity、Fragment、 WebView | Current Page Object | Yes | If it is an Activity, pass in an Activity object instance.If it is a Fragment, pass in the Fragment object instance.It is strongly recommended to implement the ICoraoolPage interface for Activity and Fragment, and define pageName in the interface method to unify the naming method |
| properties | Map<String, Object> | Custom business parameters | No | Attach these business parameters to the current page event for offline business analysis, such as the product ID and SKU ID displayed on the current page. This method can be called at any time before the page ends to collect business parameters during operation and use. Please refer to the #event tracking timing description above |
Example code:
Map<String, Object> bizProps = new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("例如itemId", "123456789");
put("例如skuId", "987654321");
}};
CoraoolSDK.tracker.updatePageProperties(this, bizProps);2.3.3 End of page
Calling this method means that the current page has ended, all parameters have been collected, and page event submission will be triggered.
Interface definition:
public void trackPageEnd(Object pageObject);
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Type | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pageObject | Activity、Fragment、 WebView | Yes | Current Page Object | If it is an Activity, pass in an Activity object instance.If it is a Fragment, pass in the Fragment object instance.It is strongly recommended to implement the ICoraoolPage interface for Activity and Fragment, and define pageName in the interface method to unify the naming method |
Example code:
public class MyActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ICoraoolPage {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageEnd(this);
}
}2.3.4 Construct GTP parameters
Interface definition:
public String buildGtp(String gtp_b, String gtp_c, String gtp_d) ;
Parameter description:
| Parameter | Type | Whether it is necessary to | Explanation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gpt_b | string | Yes | The b bit of GTP | |
| gpt_c | string | Yes | The c bit of GTP | |
| gpt_d | string | Yes | The d bit of GTP |
Example code:
// 构造gtp参数
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp("home", "topbar", "btn_show_number");
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp("home", "topbar", "btn_new_fresh");
// 如果页面对象已经实现了 ICoraoolPage 接口,可以直接调用 getPageName() 获取GTP的B位
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "topbar", "btn_new_fresh");3. Complete example
3.1 Activity Page Example
/**
* 备注:接入方的App通过定义接口 ICoraoolPage,可以规范各个页面获取名称和ID的方式
*/
public class MyPageActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ICoraoolPage {
...
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_track_home_page);
// 选择方式1:通过putExtra传参
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id_intent).setOnClickListener(v -> {
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "topbar", "btn_checkin");
Intent intent = new Intent(HomePageActivity.this, ListPageActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, gtp);
intent.putExtra(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值");
HomePageActivity.this.startActivity(intent);
});
// 选择方式2:通过构造Uri传参
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id_uri).setOnClickListener(v -> {
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "topbar", "btn_checkin");
Uri uri = Uri.parse("protocol://your.uri?k1=v1&k2=v2").buildUpon()
.appendQueryParameter(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, gtp)
.appendQueryParameter(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值");
.build();
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
});
// 选择方式3:在点击事件里增加gtp参数
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id_click).setOnClickListener(v -> {
// 先提交点击事件
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "topbar", "btn_checkin");
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, gtp);
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值");
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click("TopbarButtonCheckIn", eventValue);
// 再执行页面跳转
Intent intent = new Intent(HomePageActivity.this, ListPageActivity.class);
HomePageActivity.this.startActivity(intent);
});
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageStart(this);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageEnd(this);
}
@Override
public String getPageName() {
return "home"
}
}3.2 Fragment page example
The lifecycle callback and Activity during fragment switching are different. The system will first call the creation method of ToFragment and start it, and then call back the end and destruction methods of FromFragment. In response to this situation, the SDK has made compatibility processing.
/**
* 备注:接入方的App通过定义接口 ICoraoolPage,可以规范各个页面获取名称和ID的方式
*/
public static final class MyPageFragment extends Fragment implements ICoraoolPage {
@Override
public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View root = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_track_tab, container, false);
// 选择方式1:通过Bundle传递gtp参数
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
String gtp = ;CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "topbar", "btn_checkin")
bundle.putString(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, gtp);
bundle.putString(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值");
MyFragment fragment = new MyFragment();
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.fragment_container, fragment).commit();
});
// 选择方式2:在点击事件里增加gtp参数
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
// 先提交点击事件
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "item", "1");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, gtp);
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值");
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click("GotoNextFragment", eventValue);
// 再执行切换Fragment
Fragment toFragment = new Fragment();
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.fragment_container, toFragment)
.commit();
});
return root;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageStart(this);
}
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause();
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageEnd(this);
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
}
@Override
public String getPageName() {
return "Category";
}
}3.3 TabView Page Example
/**
* 备注:接入方的App通过定义接口 ICoraoolPage,可以规范各个页面获取名称和ID的方式
*/
public static final class MyPageTab extends TabLayout implements ICoraoolPage {
private void onCreateTab() {
// 选择方式2:在点击事件里增加gtp参数
findViewById(R.id.you_view_id).setOnClickListener(v -> {
// 先提交点击事件
Map<String, Object> eventValue = new HashMap<>();
String gtp = CoraoolSDK.tracker.buildGtp(getPageName(), "item", "1");
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTP, gtp);
eventValue.put(CoraoolLibConst.KEY_GTC, "四位gtc构成的值");
CoraoolSDK.tracker.click("GotoNextTabt", eventValue);
// 再执行切换TabView
...
});
}
/** 在Tab页出现的时候调用此方法 */
private void viewAppear() {
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageStart(this);
}
/** 在Tab页消失的时候调用此方法 */
private void viewDisappear() {
CoraoolSDK.tracker.trackPageEnd(this);
}
}3.4 H5 page example
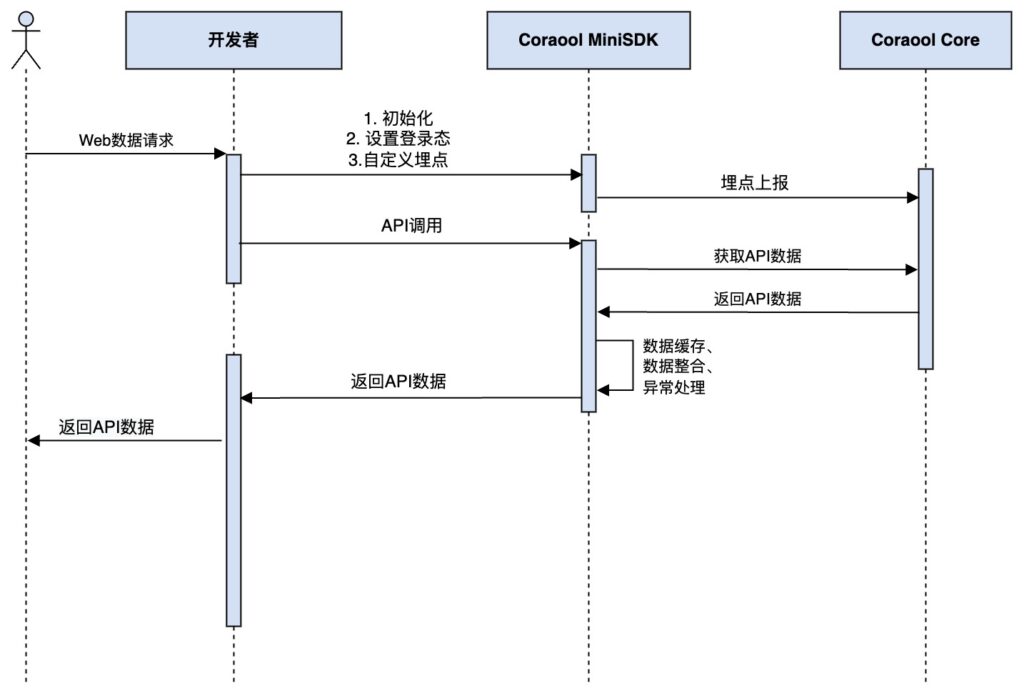
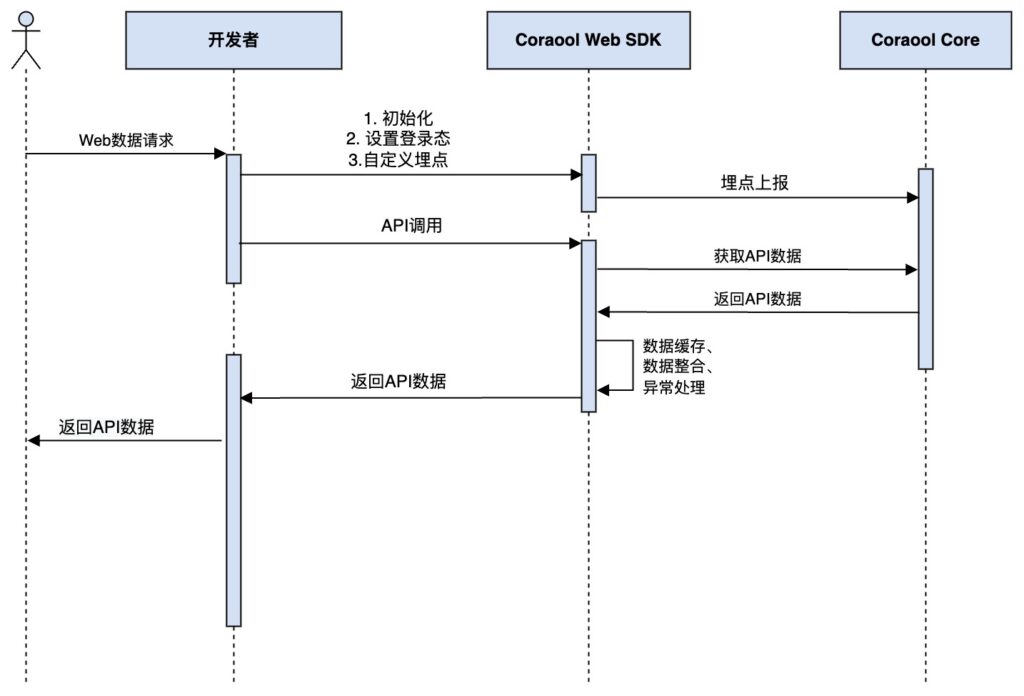
H5 pages can be redirected within a single WebView, which can use Activity or Fragment as containers. The SDK cannot perceive the page’s redirection timing, so the GTP and GTC records for H5 pages are completely controlled by H5. The API for page events is called through JsBridge.


Comments (0)